Virtual Dermatoscope

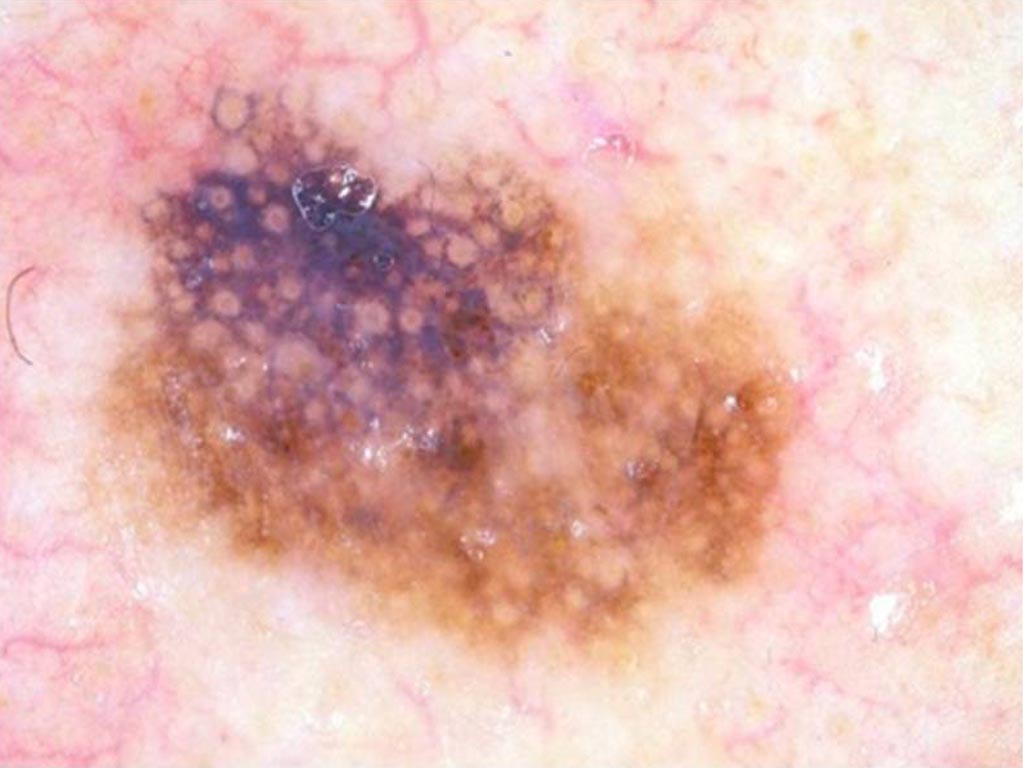
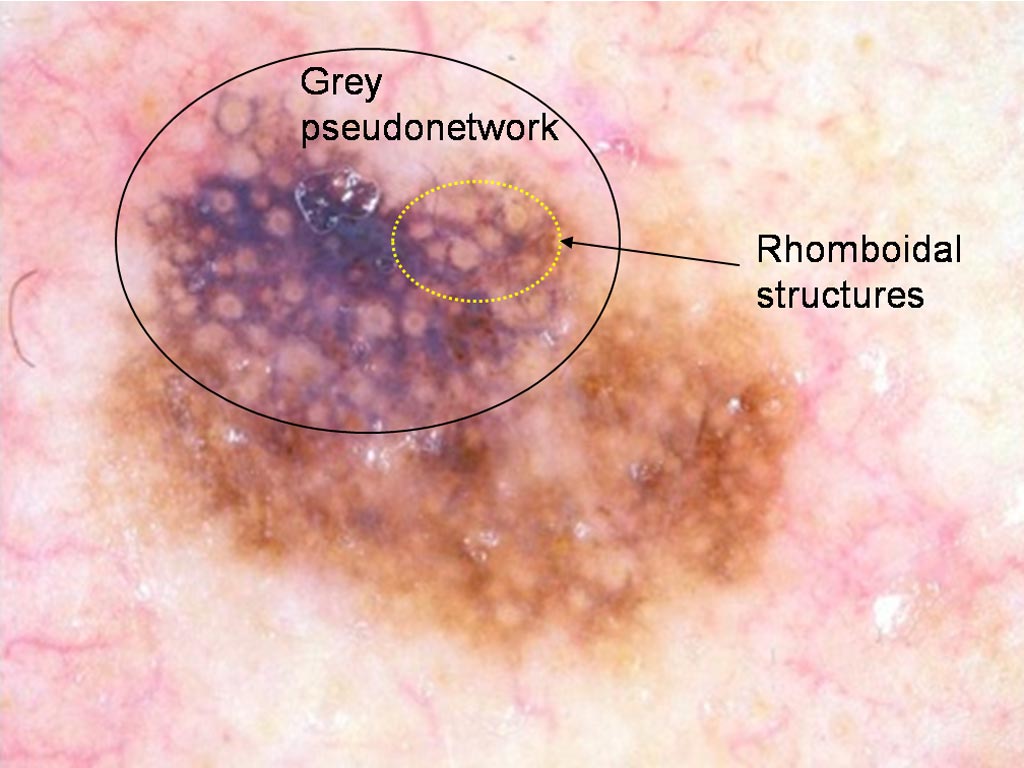
 Brown lesion on a 66 year old woman’s forehead
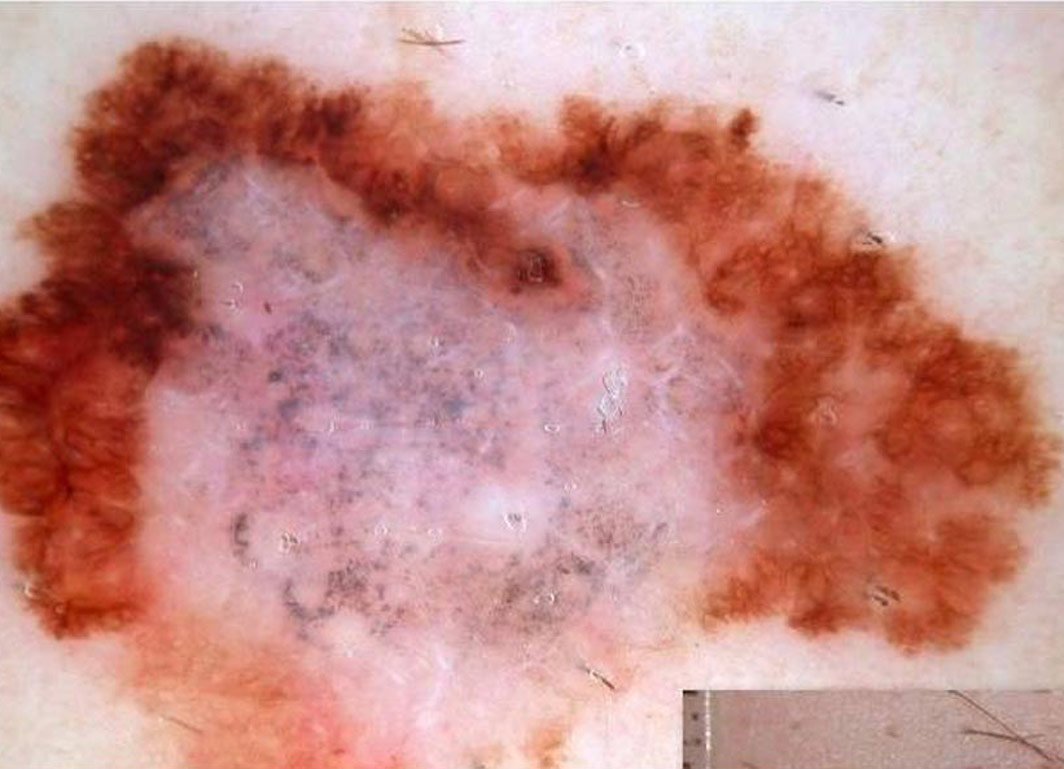
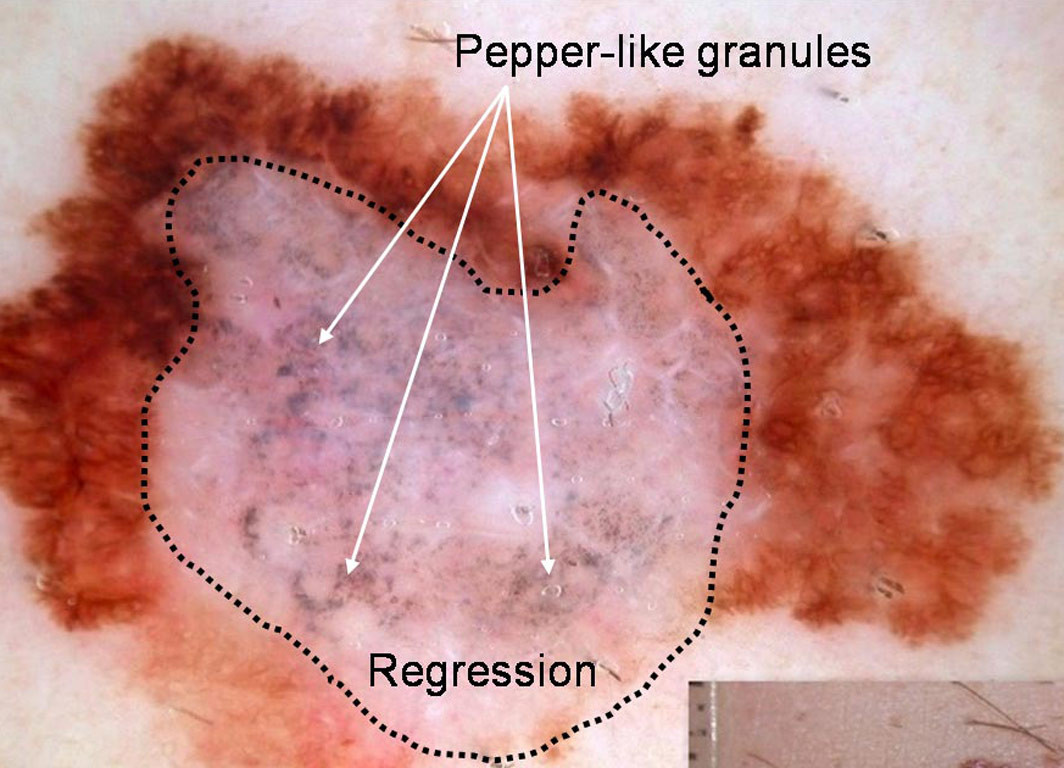
Brown lesion on a 66 year old woman’s forehead Pigmented lesion on the foot of a 58 year old man
Pigmented lesion on the foot of a 58 year old man Lesion on the face of an 80 year old man
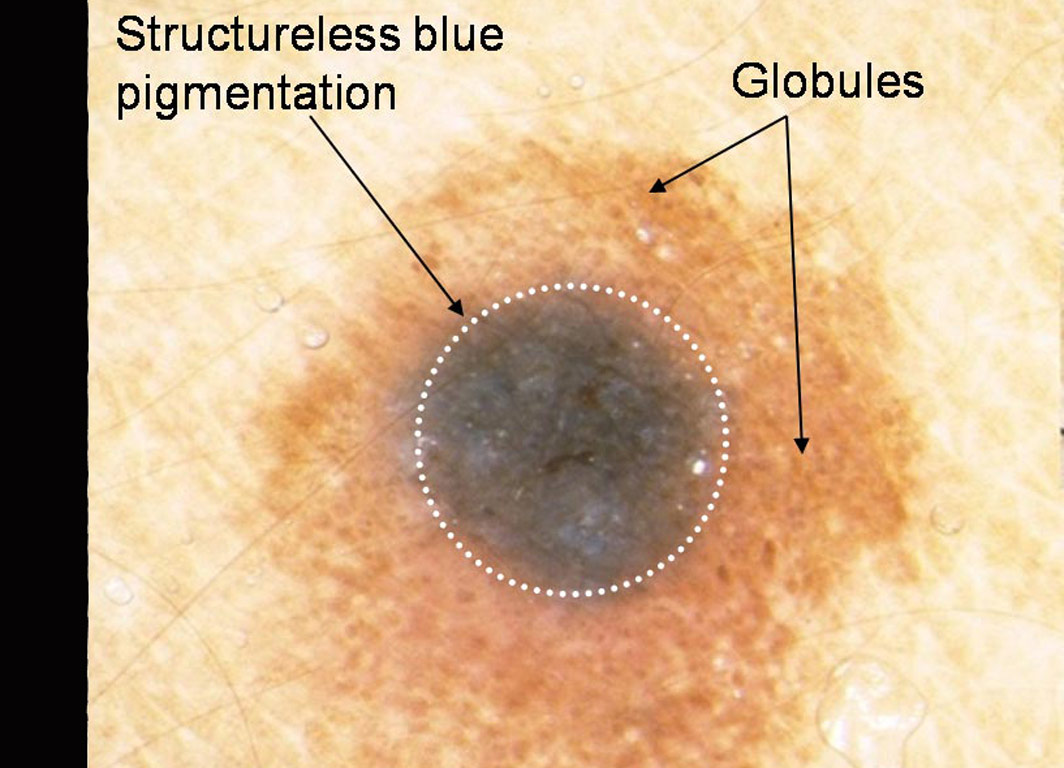
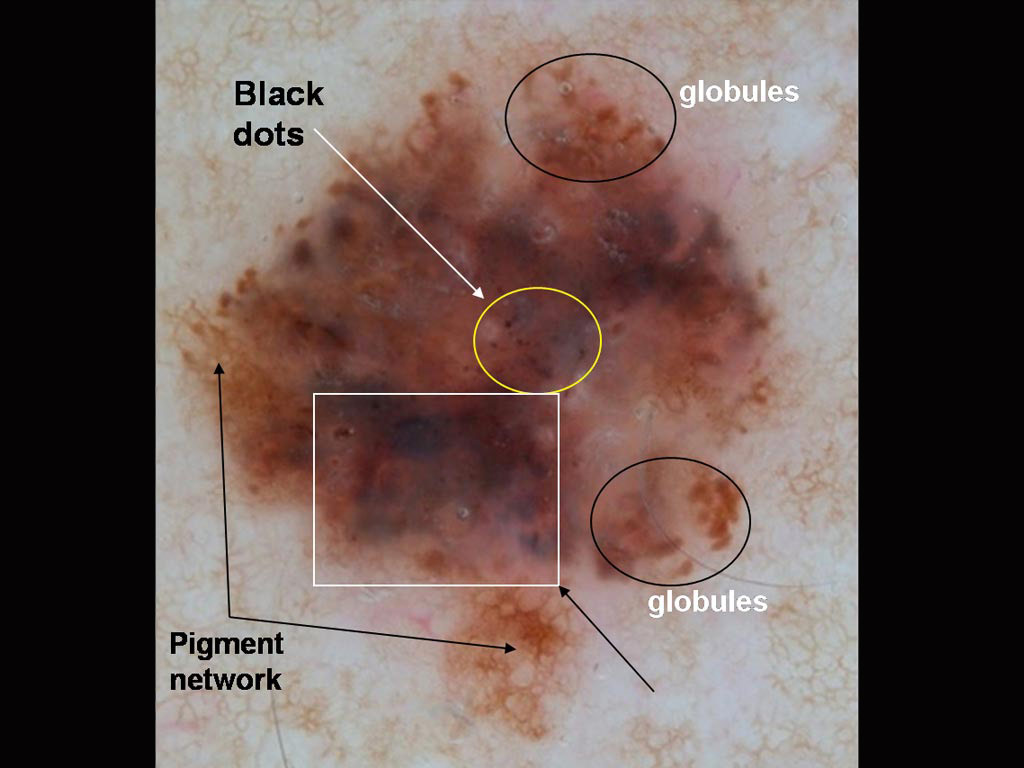
Lesion on the face of an 80 year old man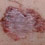 A lesion on a 58 year old woman’s thigh
A lesion on a 58 year old woman’s thigh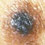 A pigmented lesion on a 36 year old man’s chest
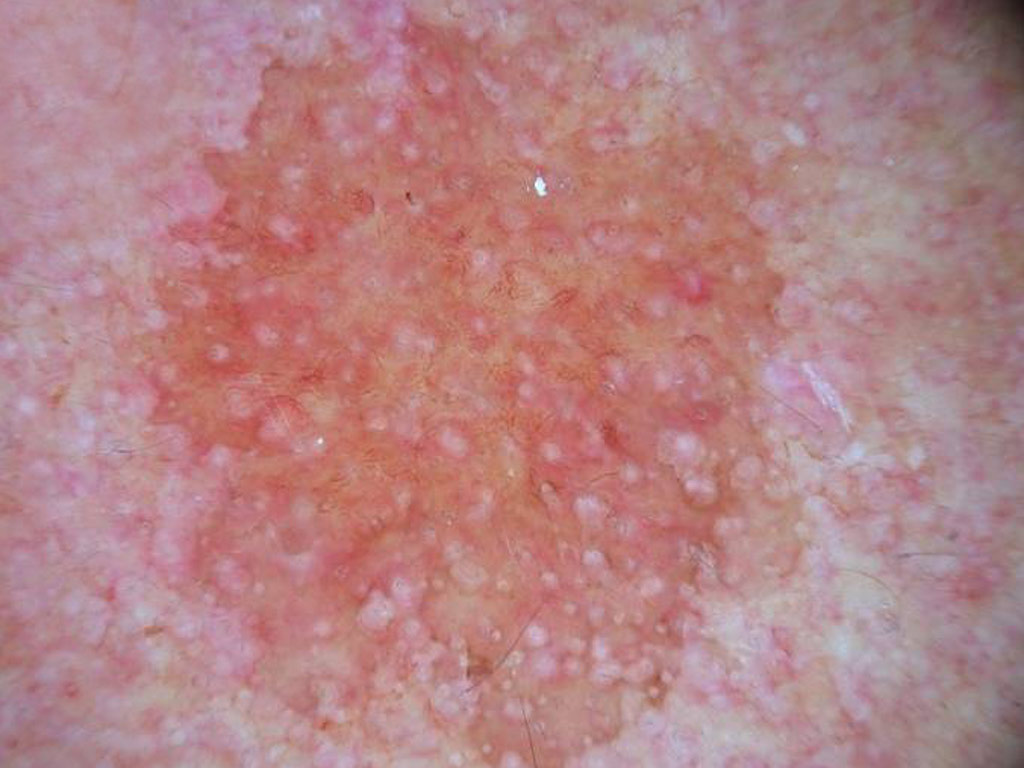
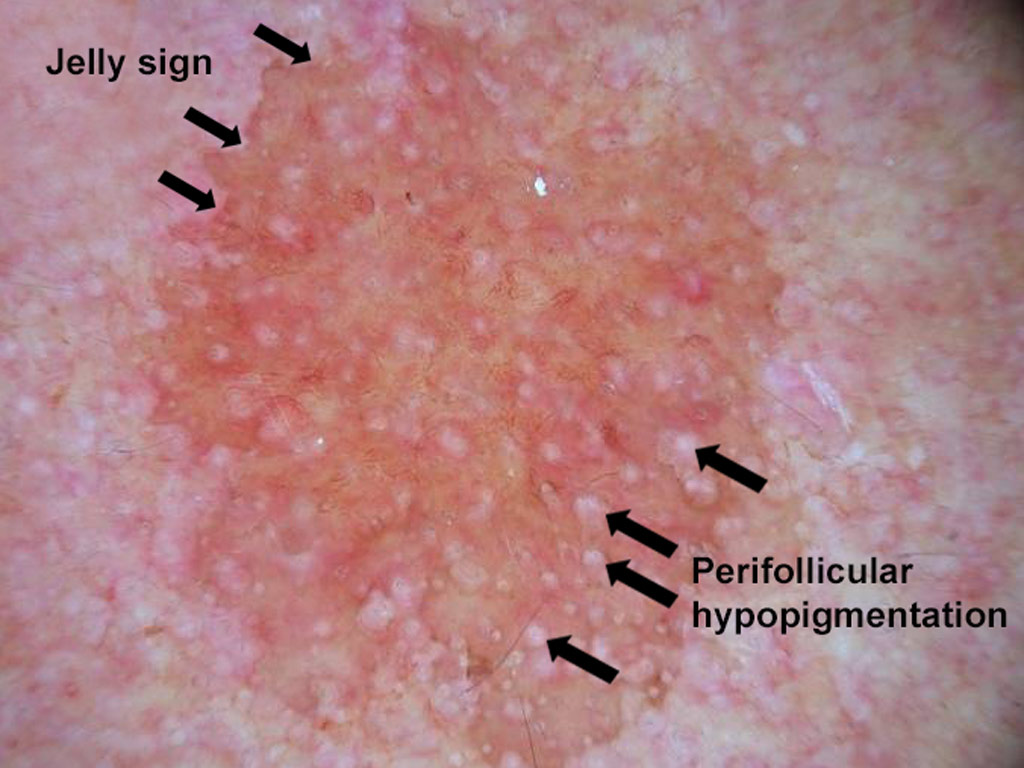
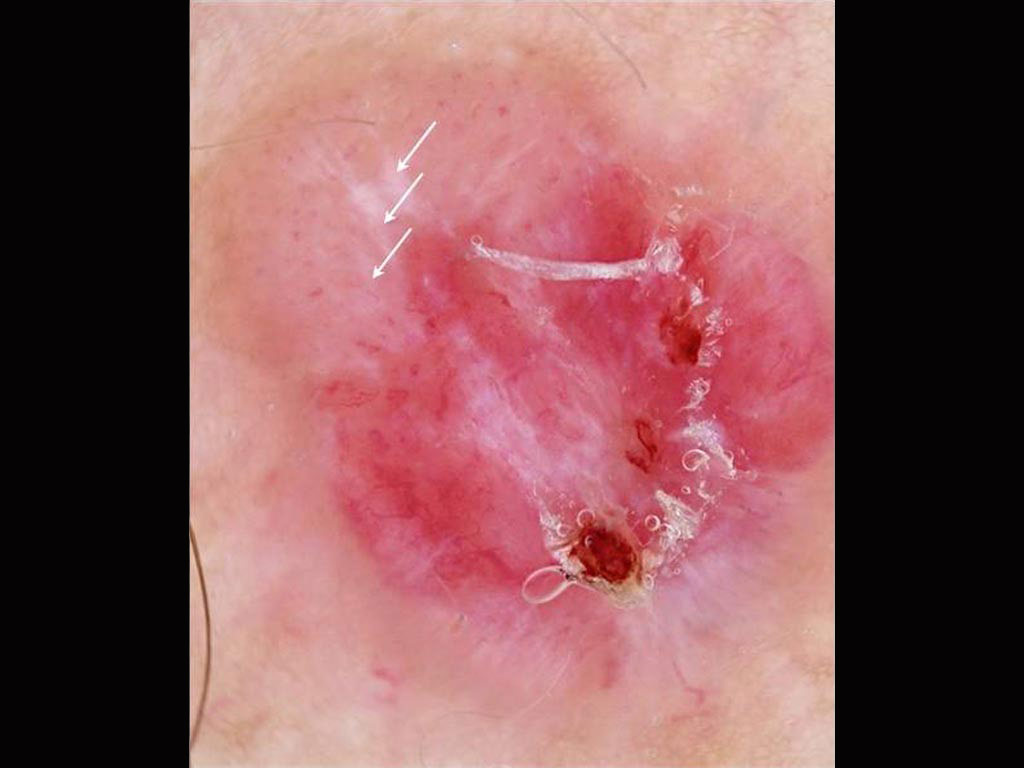
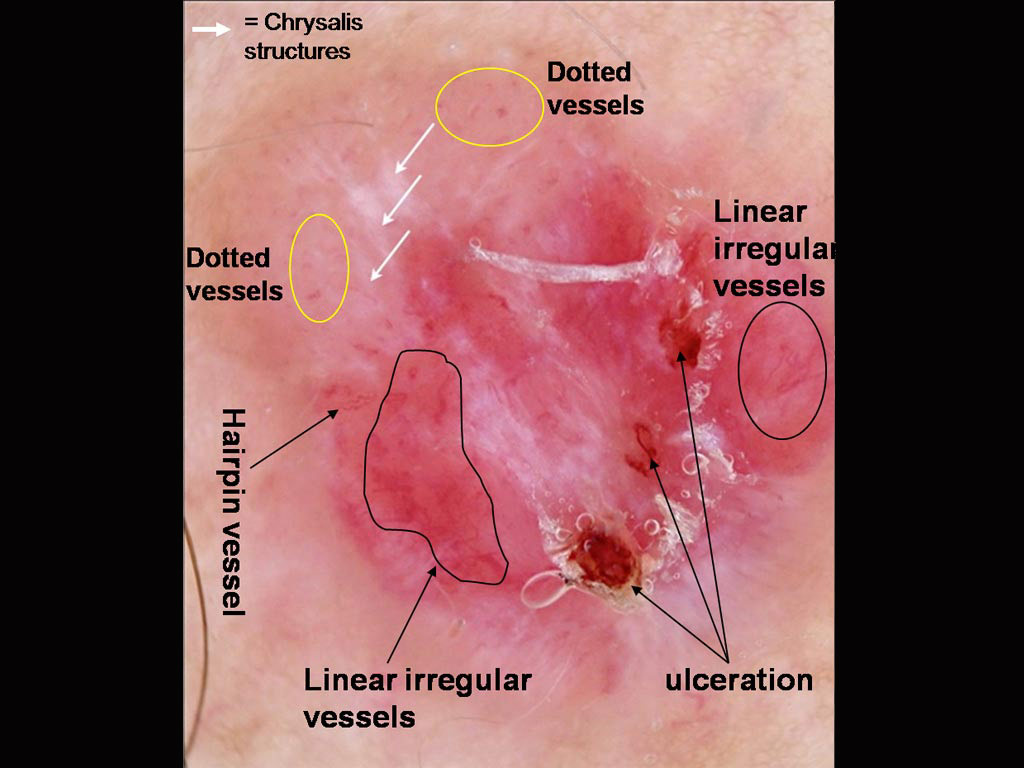
A pigmented lesion on a 36 year old man’s chest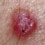 A pink nodule on a young man’s back
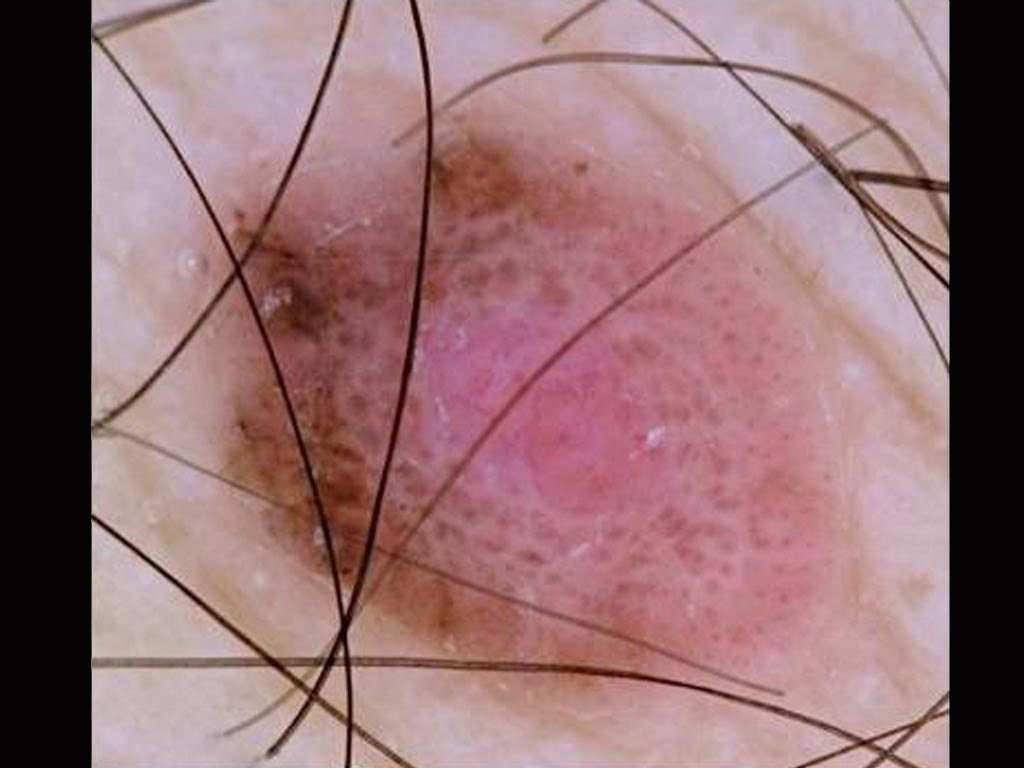
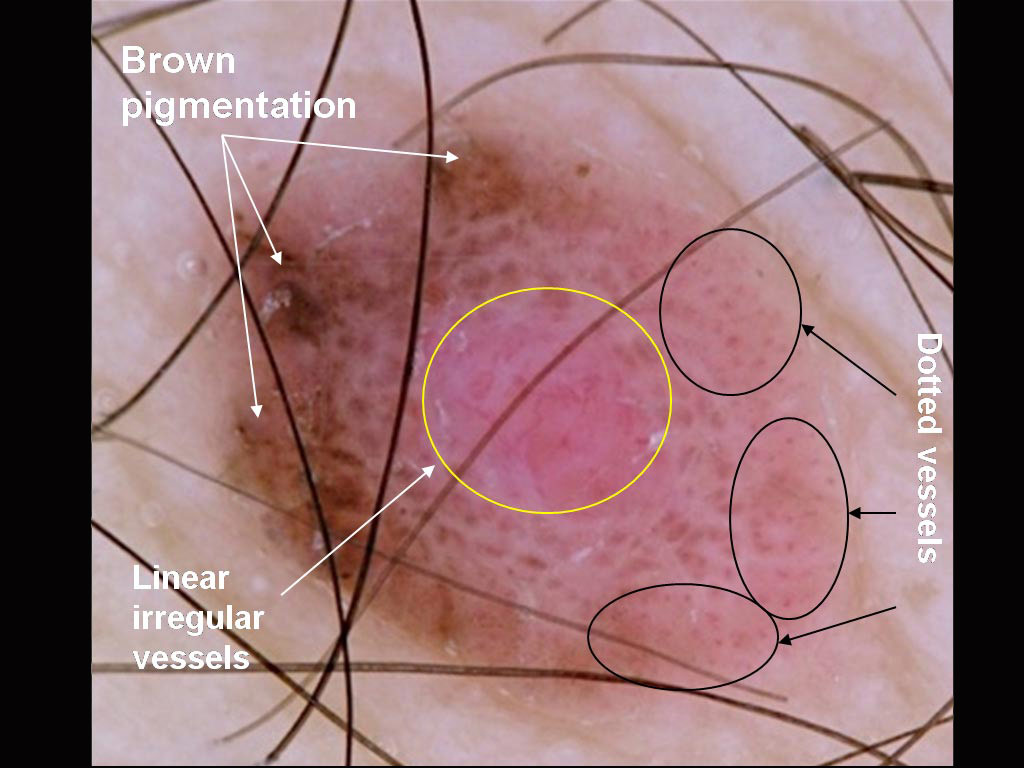
A pink nodule on a young man’s back A pigmented lesion on an elderly woman’s abdomen
A pigmented lesion on an elderly woman’s abdomen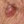 Small pink lesion on a 47 year old man’s leg
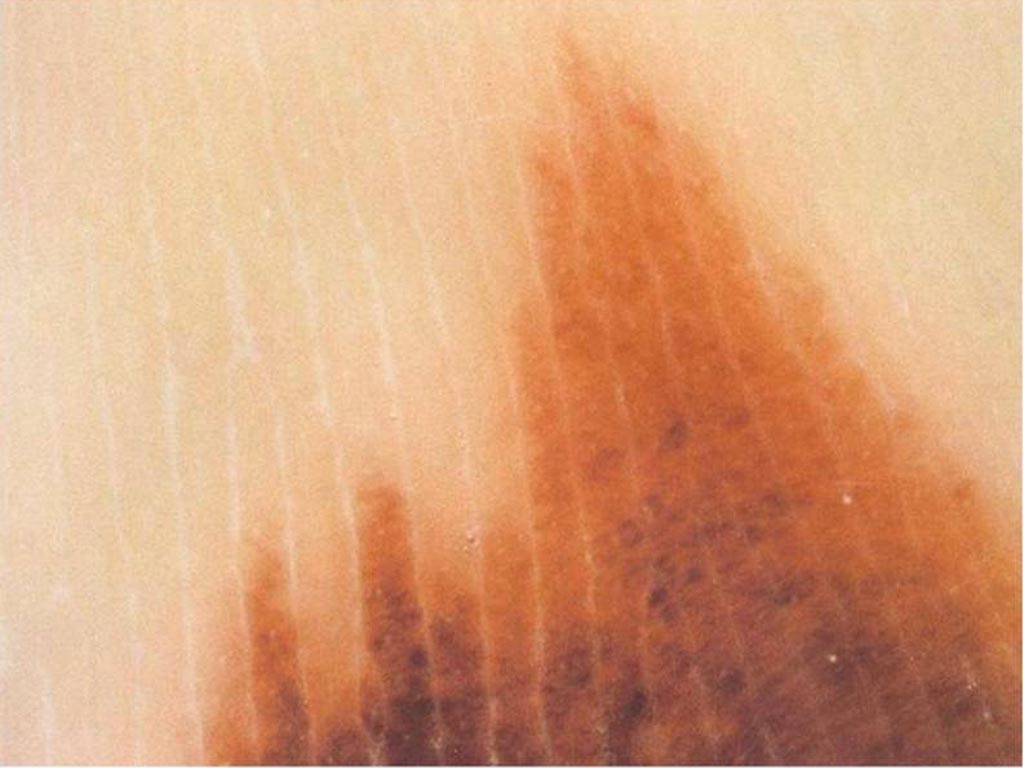
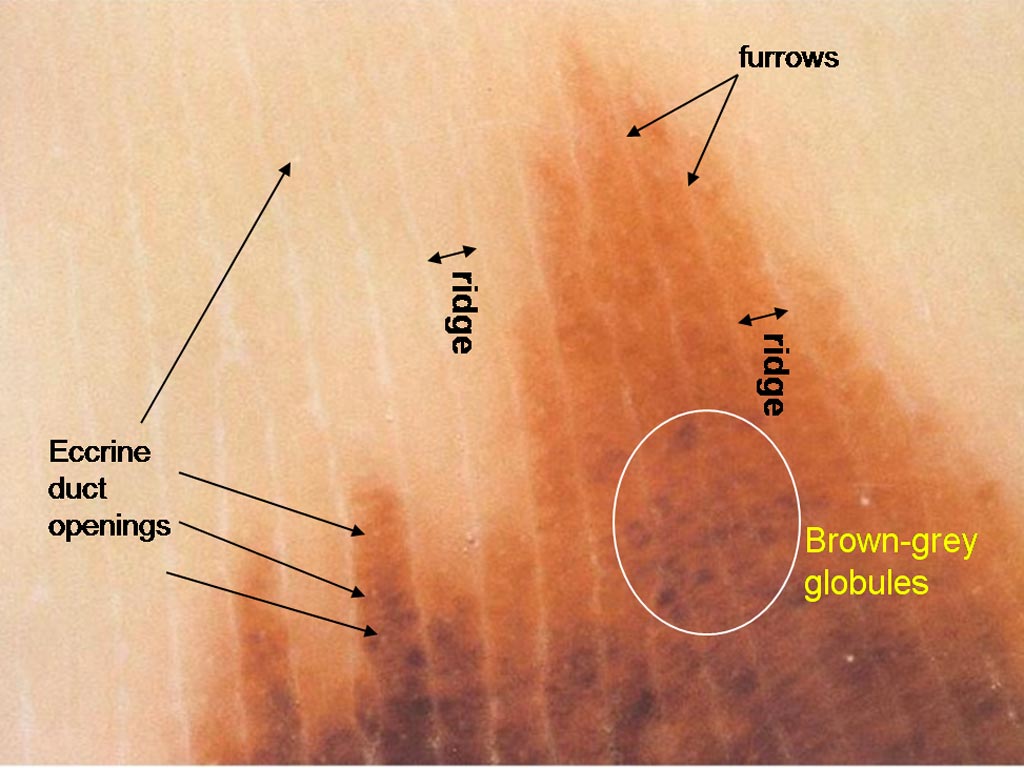
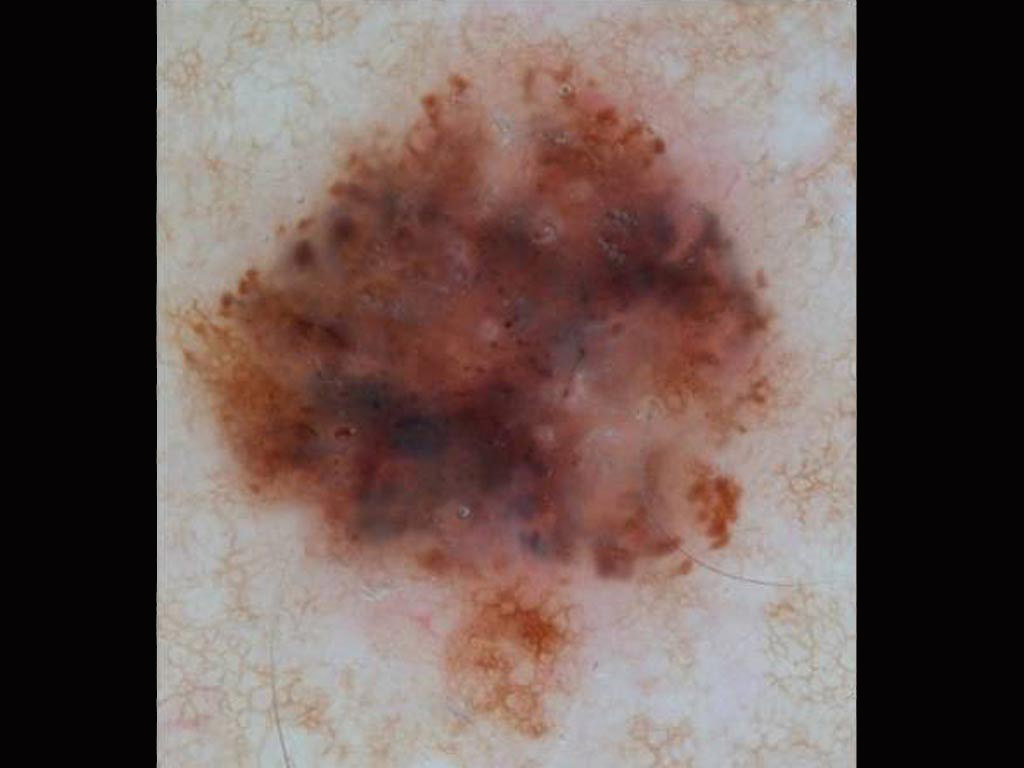
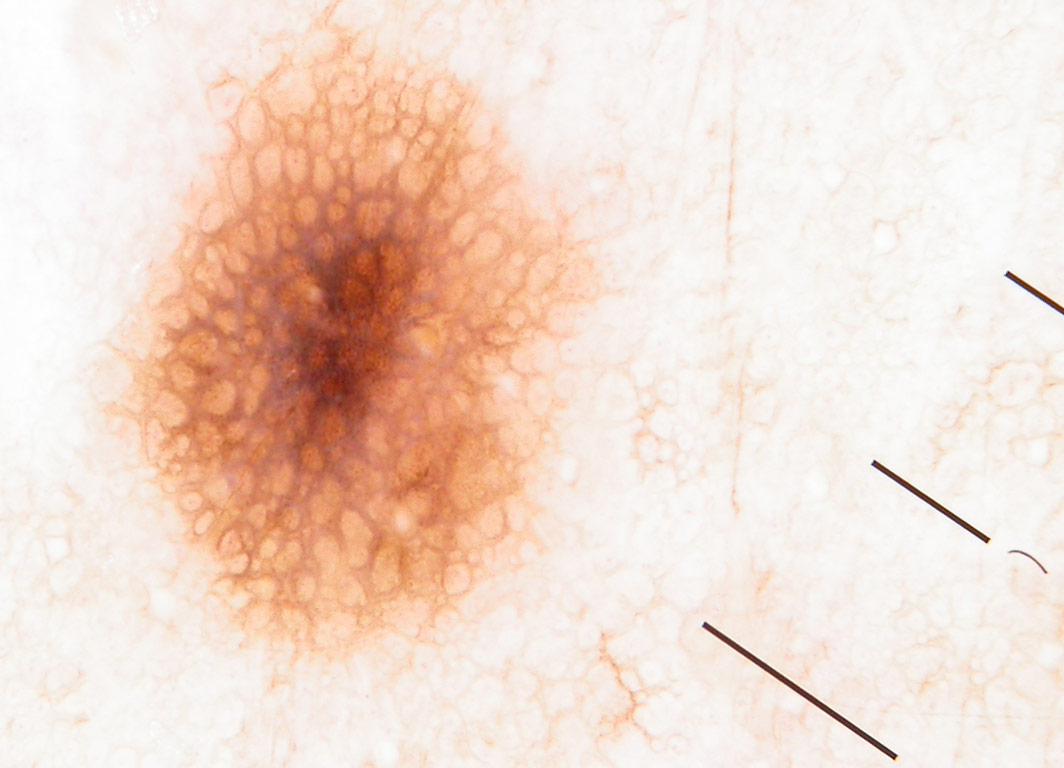
Small pink lesion on a 47 year old man’s leg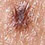 A 50 year old man with fair skin has a flat pigmented skin lesion on his abdomen
A 50 year old man with fair skin has a flat pigmented skin lesion on his abdomen